Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: Main Functions
. S Prefrontal lobes are key structures for the regulation and control of human behavior. They are critical for integrating cognitive, motivational and emotional information. Since they are connected with almost all areas of the brain, they play an essential role and are therefore often the subject of study. Between the prefrontal lobes we find the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, an area whose functions are vital to human behavior.
The frontal lobes allow us to be autonomous, facilitating much of the control we have over our life. All through the so-called executive functions, which determine the construction of our identity and the development of our self-awareness.
In this way, inner dialogue and communication with others are possible. Social cognition develops in these areas, from which empathy and the ability to put oneself in the shoes of others arise. This allows us to predict the behavior of others, anticipating their intentions, or to understand aspects such as deception.
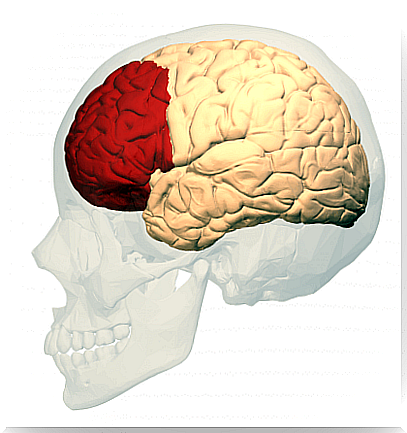
Anatomy of the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe divides into several areas:
- Motor, premotor and supplementary cortex.
- Frontal visual fields.
- Broca area.
- Prefrontal cortex.
At the same time it is divided into three regions:
- Dorsolateral.
- Orbital.
- Medial.
Main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Both Stuss and Knight (2002) and Tirapu and Ustárroz (2012) indicate some of the main characteristics of this bark:
- Inhibition, coordination and regulation of behavior.
- Search, retrieval and updating of relevant information.
- Planning, preparation and anticipation through time indicators.
- Cognitive and emotional regulation and control.
- Flexibility in changing attention and behavior depending on the circumstances.
Burguess’s team (2012) reviewed the entire scientific work concerning the main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
According to their conclusions, most of the research agreed that attention, memory, language, preparation and time sequence are the most relevant functions of this brain area. Let’s find out in detail.
Attention
Among the main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex we find attention control. The latter encompasses faculties such as switching activity, selective attention, action preparation and interference control.
Memory
As far as memory is concerned, a distinction must be made between working, or operational, and declarative memory. The first allows information to be retained and processed in a temporal manner.
Baddeley (2010) states that the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex acts as a “central executive organ”. According to the author, it has “the ability to retrieve information and keep it active while it is being manipulated.”
Stuss and Levine (2002) argue that the involvement of this area increases when the requested information “exceeds the capacity of the working memory, making it necessary to control the disturbing elements (distractors) that can interfere in the relevant information with which one is working”.
As for declarative memory, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex appears to be involved in information retrieval.
It contributes to the choice of the best strategies to encode information and helps to remember the characteristics of an event: what, when, how, where.

Alterations in source memory affect the ability to examine the source of one’s memories. This mechanism is known as reality monitoring. This allows you to discern between real or imagined events.
Baddeley assures that “a deficit in this sense may be responsible for the phenomena of proactive interference and the frequent intrusions and confabulations of patients with prefrontal lesions”.
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and language
Loss of verbal fluency is linked to prefrontal injuries, particularly of the left side. At the same time, alterations in this area would have repercussions on the narrative discourse; this is reflected in particular in the simplification or omission of grammatical forms.
Preparation and timeline
Time planning is crucial for organizing activities and days. Several researches highlight the importance of frontal areas in planning.
Arnedo, Bembibre and Tiviño (2013) affirm that preparation and temporal monitoring takes place “through the constant updating of information relating to the time necessary to carry out an action and keep it in the memory until the moment in which it is carried out”.